Have you ever encountered an issue with pages not loading in browser? Are you facing these types of problems regularly on your Windows 10 PC? If, your answer is yes then blame it to DNS cache on your PC.
DNS cache is responsible for holding critical information’s related to DNS or Domain Name System, which is responsible for any page to resolve and load in your browser. In today’s post, we will talk different ways to DNS flush or reset it in the easiest way possible.
There are Six Ways to Flush DNS on Windows 10 PC:
- From Run window
- Using Command Prompt
- Batch script
- PowerShell Command
- Reset Winsock Settings
- DNS Cache services
1) Using the Run window:
- To clear DNS to flush using Run window, press CTRL+R keys on the keyboard or Start -> In the search box -> Type “Run” -> Enter
- In the Run window, type “ipconfig /flushdns” -> enter
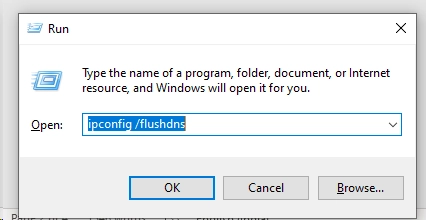
- The screen will blink, and the DNS cache will be cleaned in a blink of an eye
2) Using Command Prompt:
This is the second most straightforward way to flush DNS cache on Windows 10 PC.
- To start with the process, go to start -> look for command prompt -> right click -> select “Run as administrator” -> Enter
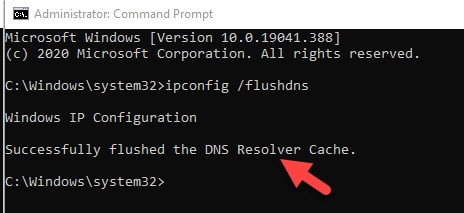
- A command prompt window will open on the screen, type “ipconfig /flushdns” without quotes and enter
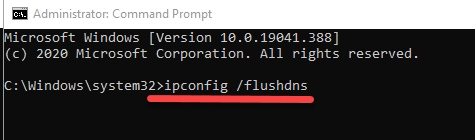
- A message like Windows IP Configuration, successfully flushed the DNS Resolver Cache will appear on the screen confirming the DNS is cleaned.
3) Using Batch Script:
In this step we are going to clean DNS using a script file, user can follow below steps to create a simple batch file.
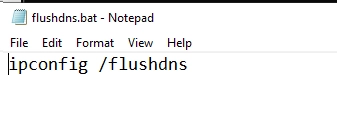
- Open a blank notepad file, by going to Start -> Search “notepad” -> enter
- In the blank notepad file, paste “ipconfig /flushdns” without quotes (as shown in the screenshot)
- Save the File by going to File -> Save as -> name the File as “DNS Flush.bat” or anything of your choice -> All files -> OK
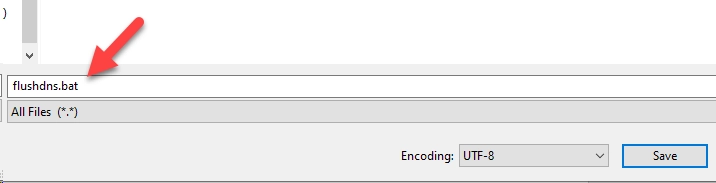
- Make sure the File ends with “.bat” extension
- Now double click on the DNS Flush.bat file to DNS flush.
4) Using PowerShell:
Resetting DNS cache that too using PowerShell is mostly favoured by Techies who love working on PowerShell script. PowerShell is an advanced version of the command prompt, and it comes with tons of loaded features.
- To start with the process, go to start -> look for Windows PowerShell -> right click -> select “Run as administrator” -> Enter
- A command prompt window will open on the screen, type “ipconfig /flushdns” without quotes and enter
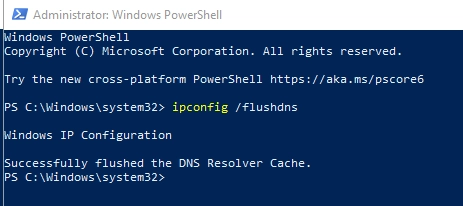
- A message like Windows IP Configuration, successfully flushed the DNS Resolver Cachewill appear on the screen confirming the DNS is cleaned.
The actual PowerShell command to flush DNS on Windows 10 or any other Windows server operating system is:
Clear-DnsClientCache5) Using Winsock Settings:
In this method, we are going to reset the Winsock settings using a command prompt. Users can use this method in case another method doesn’t help to clear DNS flush.
- Go to Start -> Search for “command prompt”
- Right-click on “command prompt” and select “Run as administrator.”
- In the command prompt screen, type “netsh winsock reset” -> enter
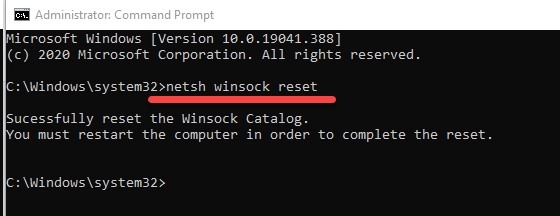
- That’s it; Windows will clear the DNS flush.
6) DNS Caching Method:
There are times when on few Windows PC, the DNS cache is not responding, and a manual restart or lookup is needed. In this method, we are going to talk more about it:
- Go to start -> search “services.msc” -> enter
- In the services window, look for “DNS Client”
- Once DNS Client service is located -> right click -> restart
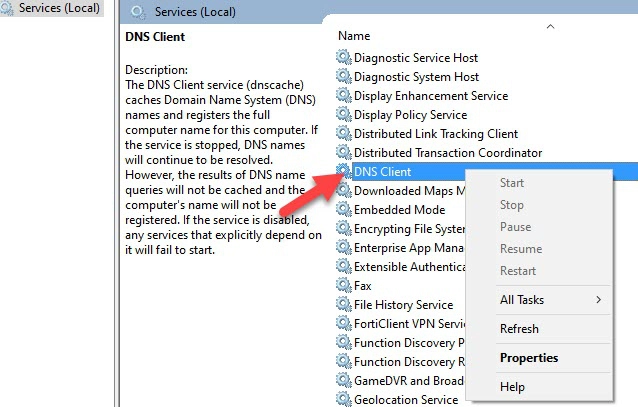
- Wait for few seconds for the DNS Client services to complete the process
- That’s it, close the services window and you can start surfing.
Note:
Some of the (mostly the latest) Windows 10 version does not allow the users to stop or start the DNS client service. There is a registry modification required to perform this. In my experience, you do not need to go this extreme level to flush DNS. If the DNS client restart option is greyed out, you can try any of the other 5 methods.
FAQ’s on Flush DNS in Windows OS:
What is DNS?
DNS stands for Domain Name Service; it is an essential feature in network topology which is responsible for converting addresses like www.google.com into a numerical address which is understood by a computer.
The computer takes the converted numerical address and tries to look for any relevant web pages available under that web address.
Usually, all web addresses are linked to an IP address, DNS does the job for resolving from web address to numerical address and vice-versa.
What is the DNS cache?
To minimize the time taken by the DNS to resolve from the main server, these days OS ( Windows or Mac or Linux) comes with DNS cache, these DNS cache stores information related to pages we access regularly and tries to resolve from it as soon we type the web address.
The cached information cannot be the same to throw out its life. Hence these caches come with an expiry also known as TTL [ time to live].
Within the TTL period, it tries to resolve the page from DNS cache.
What information does the DNS cache contain?
The information stored in DNS cache is also known as Resource Records (RR); usually, resource records comprise of the following item:
Resource data: Resource data or (rdata) contains information about the IP or host information. This information is required by the DNS to resolve from World Wide Web address to numerical address and vice-versa.
Record Type: Record type usually contains information related to the IP address of the host in IPV4 (“A”) or IPv6 (“AAA”) version.
Time to Live (TTL): TTL represents the validity record. The validity period of the TTL is counted in terms of seconds.
Class: Class in Resource Records are a group of the protocol. There are many groups available under Class. Mostly Class as “IN” is used for the internet.
Record Name: It is usually an object created to store DNS information of the host.
Resource Data Length: RD length is the information criterion of the range of resource data
Can I view the data in the DNS Resolver Cache?
Yes, the information available under DNS cache can be viewed on the PC.
To see what sits inside a DNS cache, a user must follow the below steps:
Go to Start -> Run -> Type “cmd” -> enter
In the command prompt screen, type “ipconfig /displaydns” and enter.
On the screen, it will show you a long list of all DNS cache information along with its value like: –
Record Name . . ..: skypedataprdcolweu03.cloudapp.net
Record Type . . ..: 1
Time to Live. ..: 6
Data Length. ..: 4
Section . . . . . ..: Answer
A (Host) Record . . .: 52.114.74.44
Is it safe to flush DNS?
Yes, absolutely. Frequently flushing DNS time to time will make improve computer efficiency while the internet as DNS cache is primarily used by the browser and other web applications installed on the PC to interact with the server and vice-versa.
How do I release IP and flush DNS?
To release IP, you can either restart the computer or try flushing the DNS from the command prompt in case of any internet access error.
The DNS can be flushed by going to command prompt (admin) -> and typing “ipconfig /flushdns” -> enter.
How long does it take to flush DNS?
As soon you flush the DNS using command prompt or PowerShell the old DNS cache is removed, and new cache file starts to create.
Why is a regular DNS flush useful?
All internet-connected devices these days keep some locally those are fetched or access from the server often. In such a scenario, it helps end-user to get what they are looking for fast, and on the other hand, it also keeps adding a fresh copy of cached information.
This cached information also expires after some time, and it needs to be refreshed or cleaned.
In modern OS, the system often runs a scan and fix such issues, but there are multiple instances wherein users have complained, and a manual search and fix operation is required.
In these kinds of situations, flushing DNS on regular interval keeps the system up to date.
We have tried to cover all possible ways to clear, reset and flush DNS in Windows 10 (which is applicable for Windows 8.1, 7 and server versions like Windows 2016, & 2019), do let us know in case we have missed any method or let us know which method you tried and liked in your comments below.